Delve into the fascinating realm of weathering erosion and deposition worksheet answer key, where the forces of nature shape our planet’s landscapes. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricate processes that sculpt mountains, carve canyons, and mold coastlines, providing a deeper understanding of the Earth’s dynamic systems.
Uncover the secrets of weathering and erosion, the relentless forces that break down rocks and transport sediments. Discover the factors that influence their rates and witness their profound impact on the environment. Delve into the concept of deposition, the process that transforms eroded materials into new landforms.
Explore the diverse depositional environments and the factors that shape their characteristics.
Weathering and Erosion
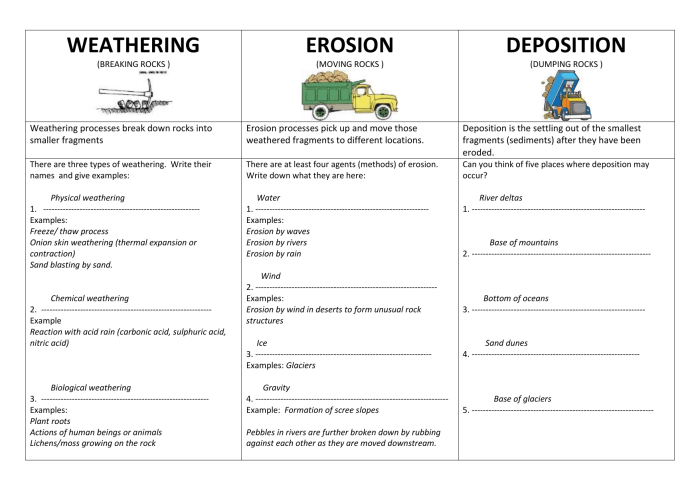
Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks and minerals into smaller pieces. Erosion is the process of transporting these smaller pieces away from their original location. Weathering and erosion are both important processes in the formation of landscapes.
Types of Weathering, Weathering erosion and deposition worksheet answer key
There are two main types of weathering: mechanical weathering and chemical weathering. Mechanical weathering is the physical breakdown of rocks and minerals into smaller pieces. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including:* Temperature changes: When rocks are heated, they expand.
When they cool, they contract. This expansion and contraction can cause rocks to crack and break down.
Frost wedging
When water seeps into cracks in rocks and freezes, it expands. This expansion can cause the rocks to crack and break down.
Abrasion
When rocks are rubbed against each other, they can break down into smaller pieces. This can be caused by wind, water, or glaciers.Chemical weathering is the breakdown of rocks and minerals by chemical reactions. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including:* Water: Water can dissolve minerals in rocks, which can cause the rocks to break down.
Acids
Acids can also dissolve minerals in rocks, which can cause the rocks to break down.
Oxygen
Oxygen can react with minerals in rocks, which can cause the rocks to break down.
Factors that Influence the Rate of Weathering
The rate of weathering is influenced by a variety of factors, including:* The type of rock: Some rocks are more resistant to weathering than others. For example, granite is more resistant to weathering than limestone.
The climate
Weathering is more rapid in warm, humid climates than in cold, dry climates.
The presence of vegetation
Vegetation can help to protect rocks from weathering by absorbing water and reducing the amount of wind and sunlight that reaches the rocks.
General Inquiries: Weathering Erosion And Deposition Worksheet Answer Key
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
Weathering breaks down rocks into smaller pieces, while erosion transports these pieces away.
What are the main types of weathering?
Mechanical weathering (physical breakdown) and chemical weathering (chemical alteration).
How does deposition occur?
When the energy of a transporting agent (e.g., water, wind) decreases, the eroded materials are deposited.